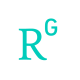IMPACT ON THE ENERGY MARKET
The ultimate impact of SCARABEUS is to introduce a step change in the current paradigm of CSP technology which, if the current techno-economic scenario remains, will progressively be less competitive compared to PV and wind technologies. The SCARABEUS concept will tackle CSP costs at their very heart by enabling significant size reductions of all the components of the plant (power block, solar field and thermal energy storage system), thus bringing about a significantly lower LCoE. The successful completion of SCARABEUS is expected to contribute to a new scenario of the Energy sector in Europe wherein this new renewable energy technology will ensure dispatchability and cost competitiveness simultaneously. This has not yet taken place since PV and wind are cost-competitive (LCoE between 60 and 100 €/MWh) but not dispatchable, whilst state-of-the-art CSP is dispatchable but has significantly higher costs (~150 €/MWh). In fact, the economic comparison between the technologies is not consistent as CSP includes a TES whose specific cost is between 20 and 40 €/kWh , while battery costs (not accounted in the LCoE of PV and Wind) are around 200 €/kWh. In addition to the lower cost than batteries, no shortage of the raw material supply for CSP plants is expected, while some studies outlined the uncertain reserve availability and resource depletion for lithium or rare earth metals which casts doubts on the overall security of supply and sustainability of battery deployment.
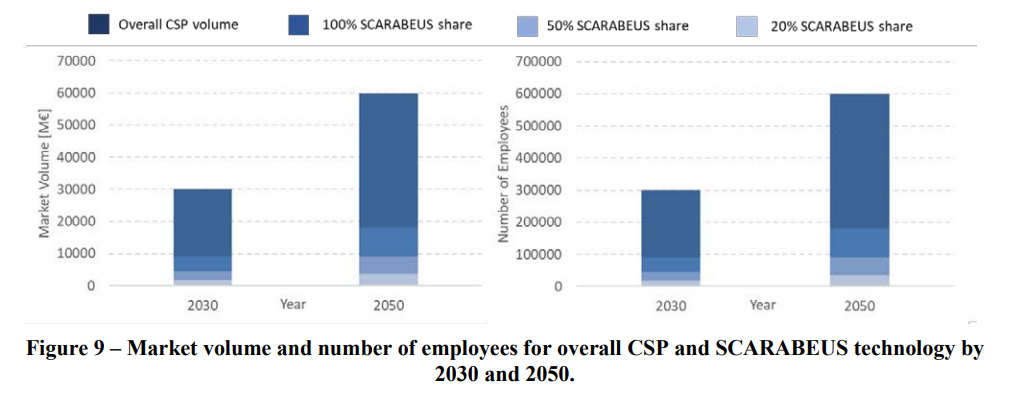
Indeed, dispatchability sets CSP apart from other technologies with regards to increasing renewable energy penetration and reduction of curtailment. This has been confirmed by a study carried out by IEA and IRENA where it is claimed that the overall installed capacity of CSP will increase from 4 GWel to 100 GWel by 2030 and 300 GW by 2050, resulting in an annual installed capacity of 10 GWel in 2030 and 20 GWel in 2050. According to these figures, and assuming a specific capital cost of a CSP plant of 3000 €/kWel (therefore with a further reduction with respect to the SCARABEUS target as a consequence of improvements in components other than the power block), the annual CSP market volume will reach 30,000 M€ and 60,000 M€ by 2030 and 2050 respectively. The market size and number of jobs that will be created by SCARABEUS as a function of technology penetration are reported in the figure below, where the SCARABEUS share refers to the overall CSP market adopting the SCARABEUS technology (this assessment is based on the assumption that the power block accounts for 30% of the overall CSP plant cost). These numbers translate into the estimated number of employees shown on the right-hand side of the figure below, according to the assumption that one employee corresponds to an annual investment of 100 k€ (value indicated by industrial partners). In the optimal case where SCARABEUS is applied to all the new CSP plants installed, the number of employees that are related to the SCARABEUS concept will be 90,000 and 180,000 in 2030 and 2050, respectively.
Market volume and number of employees for overall CSP and SCARABEUS technology by 2030 and 2050
It must be noted that the development of a new solar technology where dispatchability and cost effectiveness are combined (as it is the case in SCARABEUS) will certainly boost these figures beyond the forecasts reported by IEA/IRENA. Finally, as already anticipated in the previous section, SCARABEUS technology can also be applied to other power generation concepts and the market of these were not accounted for in the previous charts. Therefore, the number of employees and market volume could increase further with respect to the numbers reported in the figure.